The Advantages of 48V Electrical Systems in New Energy Vehicles
As automobiles grow ever more intelligent and energy-efficient, their electrical backbones must evolve to keep pace. At the forefront of this evolution is the shift from 12V to 48V systems, a transformation that redefines efficiency, safety, and power delivery.

Why the Shift to 48V Systems?
Modern vehicles host an expanding array of power-hungry technologies—advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), automated driving modules, infotainment platforms, and always-connected interfaces. The traditional 12V framework struggles under this burden. Higher current demands force manufacturers to use bulkier wiring harnesses, driving up both cost and weight.
By elevating voltage to 48V, the same power can flow with significantly reduced current. This simple yet profound adjustment trims wiring mass, lowers material expenses, and enhances overall system performance. Efficiency gains are not merely incremental; they reshape the vehicle’s electrical architecture for future scalability.
Impact on Vehicle Electrical Systems and Connections
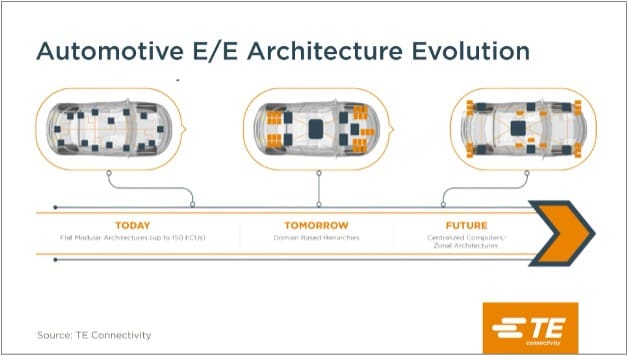
Transitioning to 48V requires connectors and cabling that withstand greater voltage stress while ensuring compactness and reliability. Early adoption centers on high-power applications, but the migration is increasingly harmonized with zonal architecture—where electronic control units (ECUs) are organized by physical location rather than by function. This design simplifies harnessing, reduces complexity, and bolsters maintainability.
Compatibility is achieved through either modifying existing connector families by adjusting creepage distances and spacing, or by employing larger connector housings for denser terminal layouts. Both strategies ensure insulation integrity while preparing vehicles for seamless 48V integration.

Unique Challenges Compared to 12V Systems
Higher voltage brings higher stakes. Critical factors include creepage, clearance, and arc suppression. A 48V system, unlike its 12V counterpart, faces a greater risk of arcing during connection or disconnection—posing safety concerns and threatening component longevity.
Mitigation strategies rely on advanced engineering: arc-resistant materials, protective circuit design, and features such as first-mate/last-break contacts. Multi-point terminal designs balance current flow, reducing localized overheating. International standards, such as IEC 60664, define the parameters—voltage levels, contamination grades, altitude considerations, and material tracking indices—that guide compliant designs.
Applicability Across Vehicle Types
One of the most compelling features of 48V systems is their versatility. Unlike architectures tethered to propulsion technology, 48V integrates effortlessly with internal combustion engines, hybrids, and fully electric vehicles alike. It operates as a universal backbone, capable of supporting both legacy systems and next-generation platforms.

TE Connectivity’s Role in Advancing 48V Adoption
Global innovators like TE Connectivity are partnering with automakers to accelerate this transition. Through the development of hybrid low-voltage signal/power connectors and efforts toward standardization, TE streamlines design complexity while unlocking cross-platform compatibility.
Standardization reduces bill of materials complexity, strengthens scalability across vehicle models, and opens the door for advanced manufacturing techniques. Flexible printed circuit (FPC) and flat flexible cable (FFC) solutions, enabled by TE’s innovations, further reduce weight and conserve space without compromising performance.

What 48V Means for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles
The 48V architecture acts as a bridge and a catalyst. For hybrids, it provides an efficient middle ground between conventional 12V systems and high-voltage drivetrains. Auxiliary functions like regenerative braking and start-stop systems thrive within the 48V domain.
For battery-electric vehicles, 48V subsystems alleviate the burden on high-voltage traction batteries. By powering ADAS, infotainment, and comfort electronics, they extend driving range, enhance system longevity, and improve reliability.
Ultimately, 48V is less about muscle and more about intelligence. It fortifies the “nervous system” of the modern automobile, enabling faster, safer, and more efficient power distribution.
Conclusion
The evolution from 12V to 48V marks a pivotal step in the journey toward smarter, leaner, and more sustainable vehicles. It addresses immediate challenges—wiring mass, cost, and efficiency—while laying the groundwork for future innovations.
As global collaboration and standardization accelerate adoption, 48V systems stand poised to define the electrical architecture of tomorrow’s mobility. With pioneers like TE Connectivity driving integration, the 48V revolution is not a distant vision but an unfolding reality.
Shenzhen Gaorunxin Technology Co., Ltd